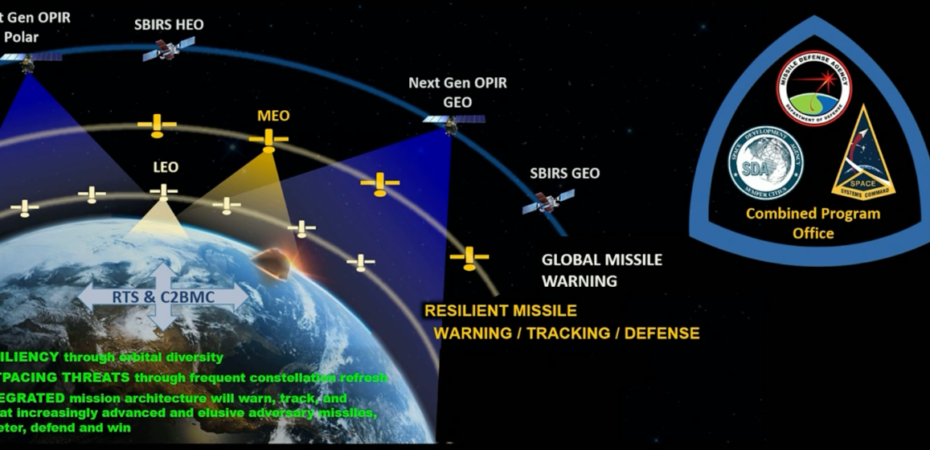
Recently, the U.S. Space Force issued a request for prototype proposals to expand its missile defense satellite network in Medium Earth Orbit (MEO). This expansion aims to deploy a new constellation of satellites equipped with advanced technologies, including Optical Cross Links (OCLs) and Overhead Persistent Infrared (OPIR) sensors. These satellites are designed to enhance missile detection capabilities, providing broader and more accurate coverage than existing systems, and improving the nation’s ability to monitor and respond to potential missile threats.
Strategic Importance
The expansion of the missile defense satellite network in MEO is vital for strengthening U.S. national security. MEO offers a unique advantage by allowing for extensive coverage and longer tracking times compared to Low Earth Orbit (LEO) systems. The deployment of these satellites enhances the U.S. military’s capability to detect and track missile threats in real-time, ensuring that any potential threats can be identified and addressed promptly. This initiative also demonstrates the U.S. commitment to maintaining its technological superiority in space, a critical aspect of modern defense strategies, particularly as global tensions rise and adversaries develop more sophisticated missile technologies.
Technical Advancements and Cybersecurity Implications and Opportunities
The incorporation of Optical Cross Links (OCLs) and Overhead Persistent Infrared (OPIR) sensors into the new MEO satellites represents a significant leap in space-based missile defense technology. OCLs facilitate high-speed, secure satellite-to-satellite communication, reducing dependency on ground stations and enhancing network resilience. OPIR sensors, on the other hand, provide continuous, real-time surveillance of missile launches, vastly improving early detection capabilities.
Given the strategic importance of these technologies, it is crucial that the Space Force integrates cybersecurity measures from the outset. With these advancements, there is an opportunity to implement robust cybersecurity protocols that protect against cyber threats, ensuring the reliability and security of the satellite network. This proactive approach will help safeguard the integrity of the missile defense system, making it more difficult for adversaries to disrupt or compromise these critical assets. By prioritizing cybersecurity in the design and deployment phases, the Space Force can ensure that these satellites serve as a strong, resilient component of the nation’s defense infrastructure.